INDIAN ARMED FORCES CHIEFS ON OUR RELENTLESS AND FOCUSED PUBLISHING EFFORTS

The insightful articles, inspiring narrations and analytical perspectives presented by the Editorial Team, establish an alluring connect with the reader. My compliments and best wishes to SP Guide Publications.

"Over the past 60 years, the growth of SP Guide Publications has mirrored the rising stature of Indian Navy. Its well-researched and informative magazines on Defence and Aerospace sector have served to shape an educated opinion of our military personnel, policy makers and the public alike. I wish SP's Publication team continued success, fair winds and following seas in all future endeavour!"

Since, its inception in 1964, SP Guide Publications has consistently demonstrated commitment to high-quality journalism in the aerospace and defence sectors, earning a well-deserved reputation as Asia's largest media house in this domain. I wish SP Guide Publications continued success in its pursuit of excellence.
- Prime Minister Modi Visits Punjab’s Adampur Air Base, Interacts with Airmen after Successful ‘Operation Sindoor’; Stern Message to Pakistan
- The layered Air Defence systems that worked superbly, the key element of Operation Sindoor
- Operation Sindoor | Day 2 DGMOs Briefing
- Operation Sindoor: India strikes back with Precision and Purpose
- Operation Sindoor: Resolute yet Restrained
- India’s Operation Sindoor Sends a Clear Message to Terror and the World – ‘ZERO TOLERANCE’
- Japan and India set forth a defence cooperation consultancy framework, talks on tank and jet engines
- Terrorist Attack in Pahalgam in Kashmir: Unfolding a long surgical war against PAK
- Lt General Pratik Sharma takes over Command of Indian Army's Northern Command
India's space sector fueling several industries
More scope for private entities, partnerships with international experts and organisations, better ability to function are strengthening India's space programme.

As the space industry worldwide is expanding and garnering attention at the rocket speed, Indian government is also pacing up to facilitate the key players of the Indian space sector. Recently Union Minister of State for Space, Dr. Jitendra Singh underlined that the Space programme offers a variety of services beneficial to any country in various domains of its development work. “India has its own priority in selected domains of space programme and is doing relatively good. The space sector reforms were made with the intention to provide level playing field for private companies and enable them to carry out end-to-end space activities,” he stated in a written reply to a question in the Lok Sabha. The government appears committed to create an ecosystem to encourage more indigenous production of space technologies, services and devices.
Private push
Since privatisation of the industry was initiated last year, the Government of India (GoI) is consistently bringing in new sector policies and guidelines while also revising existing policies.
The space sector reforms are a way to expand the national space economy, generate more employment opportunities and create better manufacturing facilities for the industry. The private sector including academic institutions, start-ups and industries can benefit from these reforms like never before, the government noted.
The Government of India received 27 proposals from private entities for undertaking various space activities in the country.
Recently, GoI also revealed that it received 27 proposals from private entities for undertaking various space activities in the country. Some of the activities include building and launching of launch vehicles, building, owning and operating satellites, providing satellites based services, establishing ground segments, research partnerships and providing mission services.
Through space-based services, launch services, manufacturing of launch vehicles and satellites, establishment of ground segment and launch infrastructure, India’s private space industry is sure to contribute in the future global space economywhich is hovering to grow over a trillion USD in the next two decades.
Space Activities Bill
The Space Activities Bill that aims at regulation and promotion of private players in space sector, is under active consideration as well by the government.
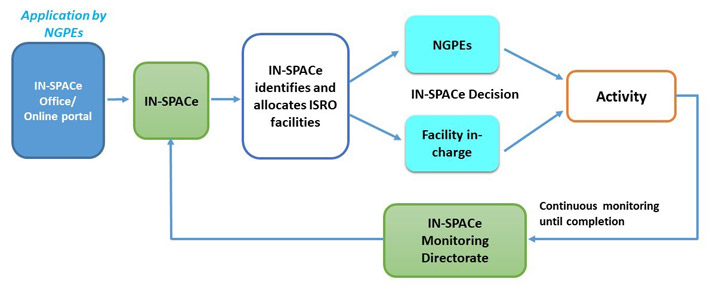
The government had announced space sector reforms in June 2020. The Union Cabinet chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi on June 24, 2020, had approved far reaching reforms in the Space sector to boost private sector participation in the entire range of space activities. Under these reforms, the establishment of an autonomous nodal agency called Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Center (IN-SPACe) under Department of Space (DOS) as a separate vertical for permitting and regulating the activities of private industry in space sector was also announced. IN-SPACe is also planned to have Safety and Security Directorate to ensure security of ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) installations when allowing access to private entities. Private entities have been given access to DOS facilities and expertise to aid their space activities. While introducing new sector policies and guidelines and revisiting existing ones, the government is also nudging for transfer of technologies developed in the field of space to Indian industries.
Space technology applications for country’s digital education
Government today said that space technology applications being used for digital education in the country. “Satellite communication is being used for beaming the educational contents in digital mode by 19 States and A&N Islands under Tele-education Programme. Further, the Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) is also beaming 51 educational channels using satellite communication.”
The Space Activities Bill that aims at regulation and promotion of private players in space sector, is under active consideration as well by the government.
Apart from this, Indian Institute of Remote Sensing is actively involved in training beneficiaries (such as UG/PG and Doctorate students, working professionals, academicians, school teachers and school students) on Space Technology and its Applications using digital platforms. During the last one year, about 2.42 lakh participants benefitted from these programmes.
The Space Sector is opened up for larger participation of non-governmental entities which is expected to bring in wide opportunities to provide space based applications including digital education.
Space Tech easing life for various sectors
Space Technology is being applied in diverse fields and sectors to bring “Ease of Living” for common man, highlighted Dr. Jitendra while interacting with senior officials from ISRO and DoS. He said, “ISRO is no longer confined only to the launching of satellites, but it has been constantly enlarging its role in development activities in the last seven years, thus contributing to Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s mission of ‘Transforming India’.”
From railways to roads and bridges, medical management/telemedicine, to procurement of timely utilisation certificates, disaster forecast and management, earth and climate studies to geosciences, urban & infrastructure to forestry and ecology etc. space technology is being applied widespread. Even during the second wave of coronavirus, leading with innovation, ISRO notably contributed by indigenously producing ventilators, helping with availability of oxygen, etc. Dr Singh mentioned, “It is not a widely known fact that ISRO had been providing Liquid Oxygen continuously on a large scale to several state governments from their own manufacturing facilities or from the existing stock during the COVID pandemic. Not only this, he said, ISRO also engaged in repurposing existing resources, scaling up of capacity of their facilities and also transferred technology to supplement the country's fight against the second wave of COVID-19, when the wave was at its peak.”
From railways to roads and bridges, medical to disaster management, earth and climate studies to geosciences, urban & infrastructure to forestry and ecology etc. space technology is being applied widespread.
Here’s how ISRO has been expanding its services to other sectors, as highlighted by the minister:
- In agriculture, satellite driven seasonal cropping pattern, experiments on yield estimation, estimation of net-sown crop area and agricultural drought assessment studies are being conducted.
- In the area of soils land degradation maps were generated that are being used to plan soil conservation/reclamation programs, land use planning, for bringing additional areas into cultivation and also to improve productivity levels in degraded lands.
- The BHUVAN portal is providing maps of salt affected and water logging area, and soil erosion maps.
- Satellite data from IRS sensors are being used to generate soil maps through monoscopic (non-stereoscopic) visual interpretation and computer-assisted digital analysis approaches
- In the field of forestry, apart from other activities, analysis of forest cover change, spatial biomass estimation, community biodiversity characterisation, forest fire alert system, inputs to working plan and wildlife plan preparation, forest carbon sequestration, inputs to UNFCCC etc. are being carried out.
- In the area of disaster management, current activities are: near real time flood & cyclone monitoring & mapping in the country, flood hazard/risk zonation for flood prone states, spatial flood early warning, forest fire alerts, landslide zonation and inventory, agricultural drought studies etc.
- On rural development, there are several initiatives/projects, which are taken up by State and Central Government departments at micro and macro level to enrich the assets required in the rural sector. For example the On Farm Water Management (OFWM), National Health Resource Repository (NHRR) Project, Rural connectivity, Sanitation, which uses the latest remote sensing and GIS technologies in operational modes.
- The usage of Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System (NavIC system) has increased in sectors like transportation and personal mobility. Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH) has mandated fitting NavIC-based AIS-140 compliant vehicle trackers in all the public and commercial vehicles. There is an increase in the number of NavIC enabled smart mobile phone models in the Indian market.
NavIC is the short for Navigation with Indian Constellation that was launched in 2012 in the sectors like transportation and personal mobility. Google Maps is an application which uses location data from Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS). Like any other GNSS, NavIC provides the location data to the map application like Google Maps. The Department believes NavIC’s performance to be on par with other non-Indian Global Positioning System (GPS). NavIC civilian signals are free-to-air and it is known to enhance the accuracy and availability of signals in the hilly terrain as well as urban canyon. In July, Garmin, a renowned manufacturer of navigation products, has launched NavIC enabled handheld devices GPSMAP 66sr and GPSMAP 65s in India.
Collaborations & expansions
This year Dr. K. Sivan, Chairman, ISRO and Secretary, DoS has been meeting various heads of space agencies from other countries, joining hands to advance the services. Earlier this year, he virtually met the President of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) and Prince Sultan bin Salman bin Abdul Aziz, Chairman of the Board of Directors of Saudi Space Commission. More recently, last month Dr. Sivan virtually interacted with AviBlasberger, Director General, Israel Space Agency (ISA), Ambassador of the Dominican Republic David Puig, and Dr. Philippe Baptiste, President, French National Space Agency (CNES).




“Chandrayaan-3 is likely to be launched during third quarter of 2022,” stated Dr. Jitendra Singh
With Blasberger, Dr. Sivan reviewed the progress of the ongoing activities including cooperation in electric propulsion system and GEO-LEO optical link. There were also discussions about potential opportunities of working together in future including launch of Israeli satellites in Indian launcher and commemorating 75th Anniversary of Indian Independence alongside 30 years of India-Israel diplomatic relations through appropriate event in the year 2022.
With Dominican Republic further technical discussions are to be held to arrive at specific cooperation proposals. While Dr. Baptiste and Dr. Sivan reviewed the progress of the ongoing cooperation activities in joint satellite missions, payload accommodation, human space flight, space situational awareness, ground stations to support satellite missions and exchange of professionals between the agencies. In April this year, Jean-Yves Le Drian, Minister for Europe and Foreign Affairs, Government of Republic of France had visited the ISRO Headquarters. An Implementing arrangement between ISRO’s Human Space Flight Centre (HSFC) and French National Space Agency (CNES) for cooperation concerning Human Spaceflight programme, specifically on sharing of expertise in space medicine, was exchanged during this visit. The Minister with his delegation has also visited ISRO’s Human Space Flight Centre (HSFC).

Dr. Jitendra Singh also recently chaired Indo-Swedish meeting on Science & Technology and Innovations with the Swedish delegation led by Ambassador Klas Molin. The minister emphasised global scientific collaboration to seek “Ease of Living” for common citizen.
ISRO is also working in collaboration with NASA for NASA’s new Earth System Observatory. In addition to that, for its first launch this year, Brazilian satellite Amazonia was launched by ISRO. This year has been a relay of collaborations and partnerships for ISRO from all across the globe, further enhancing the space programme of the nation.
These collaborations are not limited to just governments. Recently the Union Cabinet chaired by PM Modi approveda Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between Indian Institute of Space science and Technology (IIST) and The Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), the Netherlands for carrying out academic programmes and research activities involving students and faculty members in each institution.
Some major highlights of the MoU include:
- Students exchange programme
- Dual Degree/Double Degree programme
- Internships and project work
- Faculty exchange
- Joint Research
This agreement holds promise to pursue the potential interest areas of cooperation such as, exchange of faculty members, students and researchers, scientific materials, publications and information. The signed agreement will also provide impetus to explore newer research activities and application possibilities in the field of Science and Technology.
Chandrayaan-3 & other launches
“Chandrayaan-3 is likely to be launched during third quarter of 2022,” stated Dr. Jitendra Singh. The realisation of Chandrayaan-3 involves various process including finalisation of configuration, subsystems realisation, integration, spacecraft level detailed testing and a number of special tests to evaluate the system performance on earth. The progress has suffered hindrance due to COVID-19 pandemic. However, all works that were possible in work from home mode were taken up even during lockdown periods and Chandrayaan-3 is in matured stage of realisation.
Among other recent launches though, Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle-F10 (GSLV-F10) will launch Earth Observation Satellite, EOS-03 from the Second Launch Pad of Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) SHAR, Sriharikota. EOS-03 is a state-of-the-art agile Earth observation satellite which will be placed in a Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit by GSLV-F10. Subsequently, the satellite will reach the final geostationary orbit using its onboard propulsion system, ISRO informed.
The Indian space agency is also working on many other ambitious and significant missions like its first manner mission Gaganyaan, a space station as well a mission to the sun, Aditya. With the limited resources that ISRO has had in the past, its success in the industry has been appreciated around the world. With the expanding support, and meticulous work, ISRO holds strong chances to make India among the space superpower in the times to come.





